Communication System
ARINC, ACARS & CPDLC — ATPL Quick Guide
ARINC Aeronautical Radio Incorporated is a company and standards body. It defines aviation data formats and protocols (e.g. ARINC 424 for nav databases) and originally designed ACARS. ➡️ ARINC sets the rules; it is not a communication service.
ACARS Aircraft Communications Addressing and Reporting System. A datalink network/protocol that sends text messages between aircraft and ground.
- Uses VHF, HF, or SATCOM
- Used for AOC (company, maintenance) and some ATC messages
- Basis of early FANS (FANS 1/A) ➡️ ACARS is the “pipe” that carries data.
CPDLC Controller–Pilot Data Link Communications. An ATC text-messaging application for clearances, requests, and reports.
- Messages are pre-formatted and standardised (ICAO)
- Often runs over ACARS (sometimes over ATN B1 or SATCOM)
- Voice remains primary, CPDLC is secondary ➡️ CPDLC is the ATC messaging application.
- ARINC = standards & ACARS designer
- ACARS = datalink network
- CPDLC = ATC text communication application
Below is a clean, structured explanation of ARINC, ACARS, and CPDLC, keeping the distinctions precise and operationally accurate.
ARINC
What it is
Aeronautical Radio Incorporated (ARINC) is a private aviation company that:
- Designed ACARS
- Acts as a de-facto global standards body for avionics data formats and communications
Key point: ARINC defines how aviation data is structured and exchanged — it is not itself a communications network.
Role
ARINC publishes widely used avionics and data standards, including:
- ARINC 419-3 – Digital Data System Compendium
- ARINC 424-21 – Navigation System Database
- ARINC 428 – Avionics Network Design Considerations
These standards define:
- How navigation data (SIDs, STARs, approaches) are coded
- How avionics systems store, interpret, and exchange data
Summary: ARINC = standards provider and original ACARS designer, not a communications service
ACARS

What it is
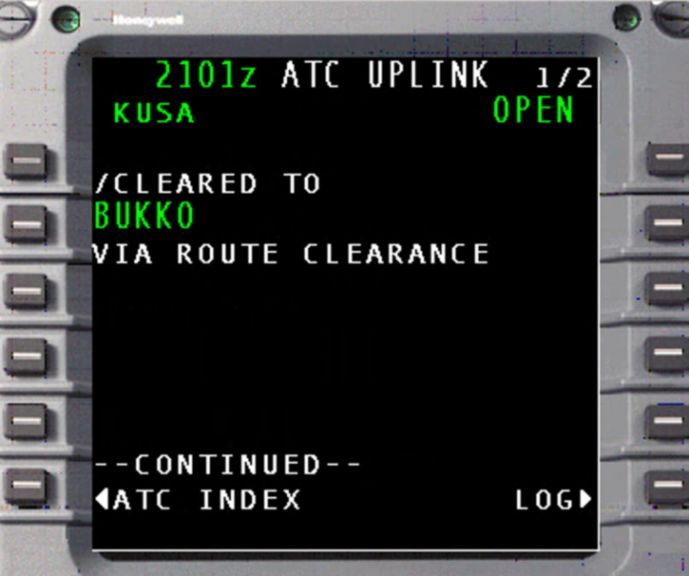
ACARS (Aircraft Communications Addressing and Reporting System) is:
- A first-generation aircraft datalink system
- Developed by ARINC
- A network + protocol, not an application
- Based on telex-style text messaging
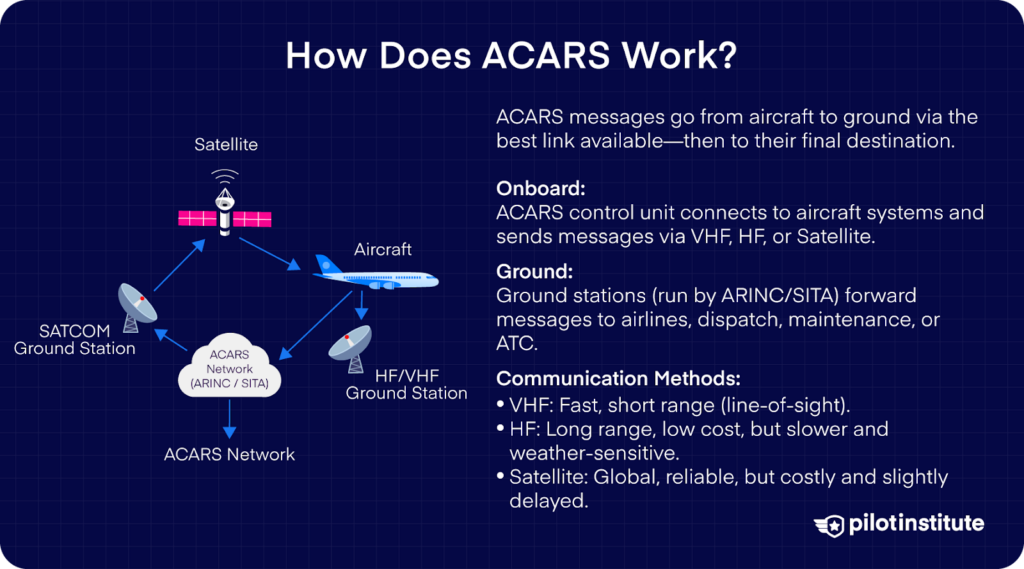
Media / communication methods
ACARS can use multiple physical links:
- VHF (line-of-sight, ~2.4 kb/s)
- HF (HFDL) – long-range, lower reliability
- SATCOM (e.g. Inmarsat)
Modern systems automatically switch between VHF, HF, and SATCOM based on availability.
What it is used for
ACARS carries messages between aircraft and:
AOC (Airline Operations Control)
- Dispatch
- Engineering
- Maintenance
ATC (in some regions and early datalink implementations)
Typical message content:
- Weather data
- Flight plans
- Administrative / commercial messages
- Engine and maintenance reports
- Event-triggered system reports
Message formats:
- Pre-formatted reports (position, faults, requests)
- Free-text messages
Place in FANS
ACARS underpins first-generation FANS (FANS 1/A) and was later adapted to:
- Carry CPDLC messages
- Support ADS-C position reporting
Summary: ACARS = the transport layer that moves aviation text data over VHF / HF / SATCOM
CPDLC

What it is
CPDLC (Controller–Pilot Data Link Communications) is:
- A software application
- Enables text-based ATC–pilot communication
- Part of the global CNS/ATM modernization concept
CPDLC defines what the messages mean, not how they are physically transmitted.
How it communicates
CPDLC can run over multiple datalink paths:
- ACARS (most common worldwide)
- ATN B1 (notably Europe)
- SATCOM
All CPDLC-equipped aircraft have VHF datalink; HF and SATCOM are optional.
Message definitions are standardized by International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) in the GOLD (Global Operational Data Link Document).
What it is used for
CPDLC handles structured ATC communications, including:
- Requests (e.g. climb, route change)
- Clearances
- Reports (especially in oceanic / non-radar airspace)
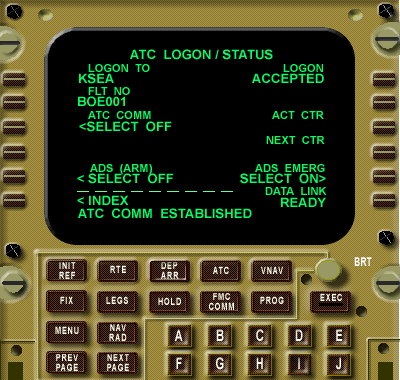
Pilot workflow example:
- Pilot enters request (e.g. CLIMB DUE WEATHER)
- System shows a VERIFY page
- Message is sent
- ATC replies with an uplink clearance
- Pilot selects ACCEPT / REJECT / STANDBY
Relationship to voice and ADS
Voice remains primary, even in Datalink Mandatory airspace
CPDLC is secondary / backup
ATC units may use:
- ADS only
- CPDLC only
- Both together
Summary: CPDLC = the ATC messaging application that often rides on top of ACARS
Putting it all together
Conceptual stack
ARINC
└─ Defines standards (data formats, protocols)
└─ ACARS
└─ Datalink transport (VHF / HF / SATCOM)
└─ CPDLC
└─ ATC–pilot text messaging application
One-line definitions
ARINC Standards body and original ACARS designer
ACARS Aviation datalink network/protocol for operational and ATC messages
CPDLC Structured ATC–pilot text communication application
ARINC vs ACARS vs CPDLC, with roles clearly separated.
✈️ ARINC vs ACARS vs CPDLC
Core Idea (memorise this)
- ARINC = standards & network provider
- ACARS = data transport system
- CPDLC = ATC communication application
1. ARINC
What ARINC is
A standards body and service provider
Defines:
- avionics standards (e.g. ARINC 429, 702)
- message formats
- ground networks
What ARINC does
- Operates ACARS ground networks (one provider)
- Provides communication infrastructure for airlines and ATC
👉 ARINC = rules + pipes on the ground
2. ACARS (Aircraft Communications Addressing and Reporting System)
What ACARS is
- An air–ground data link system
- The transport layer
What ACARS does
Carries many message types:
- CPDLC
- ATIS / weather
- AOC (airline messages)
- Maintenance data
How
- Uses VHF / HF / SATCOM
- Managed onboard by CMU / ATSU
👉 ACARS = how data is sent
3. CPDLC (Controller Pilot Data Link Communication)
What CPDLC is
- An ATC communication application
- ICAO-standardised message set
What CPDLC does
Sends:
- clearances
- instructions
- requests
- reports
Reduces voice radio use
How
- Runs on top of ACARS (or ATN)
- Requires ATC logon
👉 CPDLC = what ATC and pilots say
Side-by-Side Comparison (Exam Gold)
| Aspect | ARINC | ACARS | CPDLC |
|---|---|---|---|
| Type | Standards & network | Data transport | ATC application |
| Role | Defines & provides | Moves messages | Communicates ATC info |
| Airborne system | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ |
| Message content | ❌ | Any | ATC only |
| Replaces voice | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ (partly) |
| Depends on | — | Radios | ACARS / ATN |
Simple Analogy (Very Effective in Exams)
- ARINC = Internet standards + ISP
- ACARS = Internet connection
- CPDLC = Email messages
ARINC provides the standards and ground network, ACARS is the data link system that transports messages, and CPDLC is the standardized ATC communication application carried by ACARS.